
- Red Search
- Resources
- Email Spam Statistics
Email Spam Statistics Australia & Global (2025)
-
 Daniel Law
Daniel Law
With 347 billion emails transmitted daily, did you know that nearly 46% of all emails sent globally are spam? Opening a spam folder is like shopping online to find the best deals for products, hire services, loan offers, or even ads for miracle cures.
While these unsolicited messages often saturate inboxes, they usually contain malicious links or attachments designed to capture sensitive information. These unwanted emails clutter and fill up inboxes, suggesting why 40% of users report having at least 50 unread emails.
As 1 in 6 emails end up in spam folders, this highlights the need for brands to authenticate and secure emails to avoid being sidelined. Read on to uncover the latest trends, threats, and best practices to fortify your brands against email spam.
Key Email Spam Statistics
With 78% of users likely marking emails as spam based solely on appearance, this is a huge challenge for businesses to foster user trust and engagement in an increasingly crowded inbox.
Not to mention that nearly 1.2% of all emails sent are malicious, translating to 3.4 billion phishing emails daily. This underscores that robust security measures are critical to maintaining trust, efficiency, and integrity in digital communications.
Let’s dive deep into the scope and scale of email spam to help your business anticipate and counteract this threat looming on the other side of your inbox.
Projected daily email sends reached nearly 362 billion worldwide in 2024. Considering that over 40% of all emails year-over-year are spam, at least 145 billion daily spam emails enter all user inboxes annually.
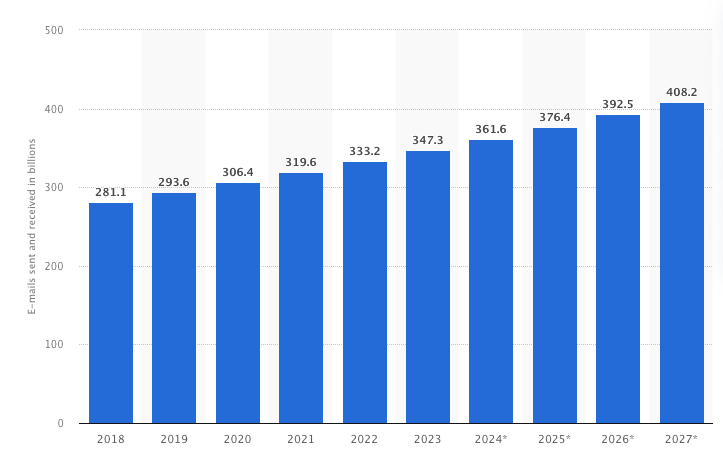
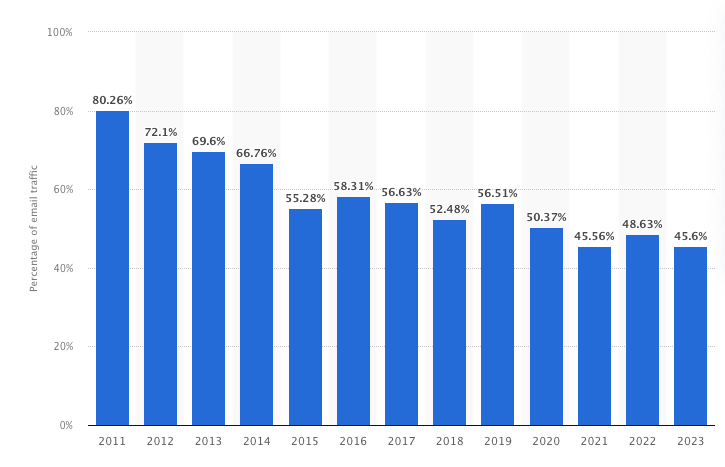
In 2023, around 45.6% of global email traffic was spam, accounting for almost 160 billion spam emails sent daily. While this figure declined by 24% compared to a decade ago, it suggests that spammers increasingly use alternative platforms for their campaigns.
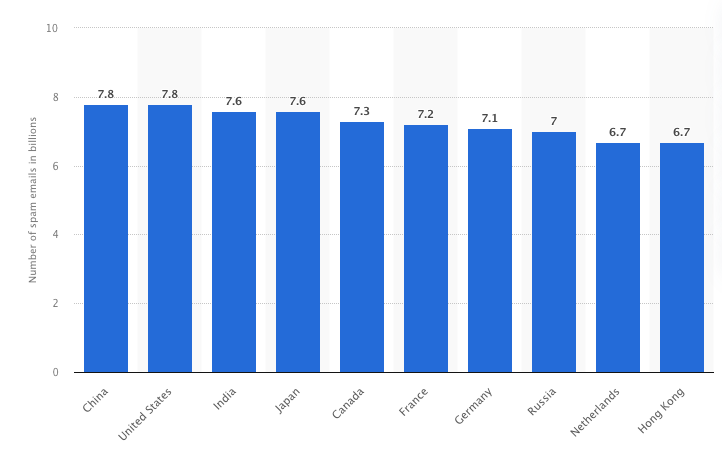
The US and China send about 7.8 billion spam emails daily, highlighting that email use remains one of internet users’ most popular digital activities. The lowest figure possible could still reach 3.8 billion spam emails daily for other countries in Q4 2024.
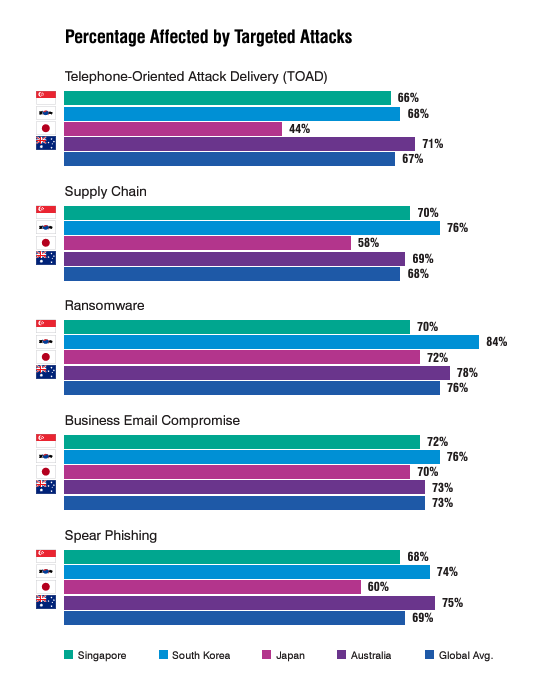
In Asia-Pacific, Proofpoint reveals that business email compromise (BEC) fell except for non-English speaking countries, which are linked to generative AI tools that can write convincing email lures in multiple languages. Despite the trend, 73% of Australian organisations still encounter BEC attacks, similar to the global rate.
 Source: APJ
Source: APJ
Mimecast reveals that 86% of detected email threats (119 million) were scams, with phishing (impersonation) lagging at 9% (12.7 million) in Q4 2023. Spam emails propelled by 13% in Q1 2024 (per user), with malicious links steadily rising in user email inboxes.
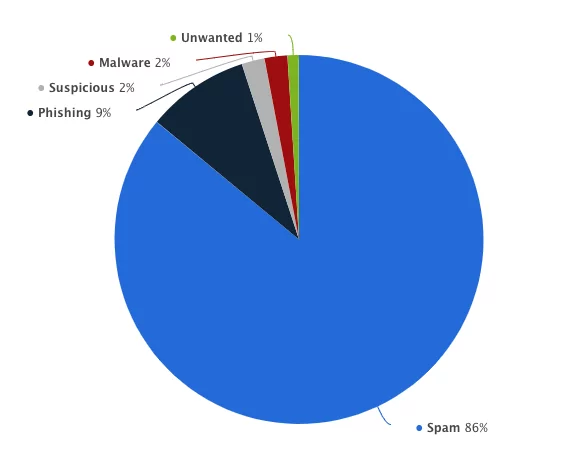
Source: Statista
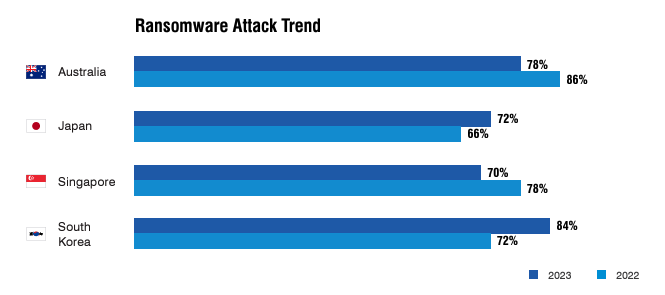
While spam may carry harmless promotions, attached malware remains a serious threat. For instance, 86% of Australian organisations encountered ransomware attacks in 2023, an uptick of 8% compared to the previous year.
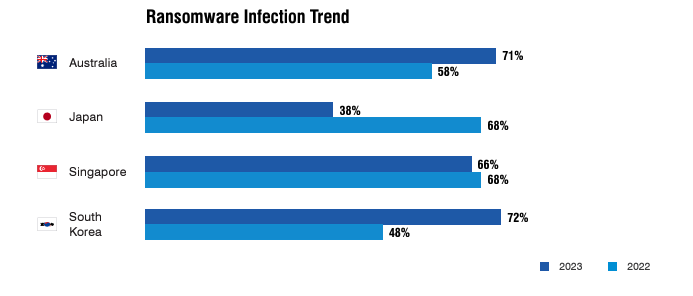
The rise in ransomware attacks drives successful data breaches and account takeovers. In Australia, for example, the high attack rate catapulted ransomware infections from 58% (2022) to 71% (2023) despite adopting robust defence strategies against cyber threats.
AIC reported that nearly 1 in 10 spam emails is malware-compromised, with URL shortening frequently used to evade detection and spread malicious content. Unfortunately, this powerful method can easily deceive tech-savvy users and anti-virus programs.
Most spam emails targeted users in the scientific & technical, legal professional services, and IT industries, receiving over 20 attacks per user in Q2 2024. Meanwhile, the IT sectors were the most targeted by phishing emails, with 208 messages per user.
G Suite (Google Workplace) redirected roughly 60% of over 1 million emails per month to the spam folder. Meanwhile, about 49% of emails from Gmail, the most popular platform, ended up in spam folders (relatively young inboxes) in Q3 2024.
What is Email Spam, and Why It’s Still a Problem in 2025
Spam email is unsolicited, irrelevant messages that unwind in your inbox. Often sent to large groups of users, this evokes user’s curiosity and trust through misleading, unverifiable content with a hard-to-find opt-out button.
As email users steadily grow by 3% year-over-year globally, email spam remains a persistent threat to business and personal communications. Here are some common types clogging your inbox:
- Phishing Emails: These deceptive messages mimic trusted brands to trick you into divulging data like passwords, credit card numbers, or social security details. In 2024, 4.8 billion phishing emails were sent daily.
- Promotional Spam: While some are harmless, these unsolicited advertisements can clutter and divert your attention from vital messages. Despite receiving as low as one response per 12 million emails, spammers continue this practice due to the sheer volume of customer reach.
- Malware & Ransomware Emails: These contain malicious links or attachments designed to infect devices with harmful software. Such cyberattacks involve corrupting data or denying file access unless you pay a ransom.
With spam on the rise, it’s crucial for businesses to understand how it affects them. Although predictive AI spam filters are projected to improve detection rates by 30% by 2025, AI-driven spam and malware has made cyberattacks more sophisticated and harder to discern.
How Email Spam Affects Businesses
Beyond clogging mail servers, a single tick to a malicious email can impact your business’ security, operations, and revenue. Let’s explore the true cost of spam across industries.
1. Email Deliverability
Modern inboxes have sophisticated spam filters that scrutinise each email for any telltale signs of spam. Once the email service provider (ESP) flags messages as spam, there’s a high chance the intended recipients may never open them.
This repeated spam report dwindles engagement rates, rendering even trusted companies’ marketing efforts virtually invisible.
In 2022, a detailed case study reported that a prominent investment firm missed a hefty $15 million deal because their spam wrongly flagged an important email as junk.
2. Cybersecurity Risks
Even though only 2% of detected email threats globally contained suspicious malware in 2023, this still accounted for 2 million emails capable of security breaches and ransomware attacks.
Corvus reported that ransomware attacks increased 95% year over year. On average, the ransom payment climbed from $212,000 (2022) to $740,000 (2023), up 250%. Meanwhile, ALPHV Blackcat group’s latest ransomware (2.0 Sphynx) had compromised over 1,000 entities in the US, collecting roughly 300 million in ransom payments in 2023.
3. Revenue Loss
When legitimate marketing emails reach the spam folders, companies face lost sales opportunities. According to the Data & Marketing Association, every dollar invested in email campaigns yields a return of up to $42, highlighting the potential losses when emails don’t reach their intended customers.
As spam email gets smarter at sneaking into users’ inboxes, no business is immune to this looming digital threat. Red Search can help you improve your email deliverability and protect your business from spam attacks.
Email Spam Trends to Watch in 2025
Email spam continues to evolve as attackers refine how they extract sensitive information. Staying abreast of these emerging trends is critical to circumventing these malicious attacks, which threaten data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Increase in AI-Generated Spam
Cyberattackers use generative AI and machine learning models to automate hyper-realistic emails with more convincing phishing lures while translating attacks to other languages.
Besides enhancing engagement, these personalised spams avoid the ESP filter better, suggesting why they can reach and entice about 60% of users, a number expected to rise in the coming years.
Rise in Smishing (SMS Spam)
With the growing reliance on mobile devices, SMS spam is rapidly gaining ground. Threat actors are exploiting the urgency associated with text messaging to deliver malicious links in bulk that easily bypass traditional email filters. As more SMS spams easily bypass network security using illegal cell sites, this social engineering attack will likely grow by 2025.
Growth in Phishing Email
Email remains the number one vector for cybercriminals, with phishing attacks being the top threat for email users.
An in-depth report highlights a 202% increase in email-based threats in 2024, with users receiving at least one advanced phishing link capable of infiltrating network security controls. Even though users are more aware of phishing tactics, spammers continue to adapt, using AI-driven tools to automate more intricate schemes.
Role of AI in Spam Detection
If gen AI supercharges the inflow of phishing emails, could it also thwart these cyber attacks?
Google, Microsoft, and other email platforms leverage AI to improve spam filters. Its machine learning algorithms analyse email patterns indicative of suspicious activities, ensuring your inbox stays safe and secure.
How to Protect Your Business From Email Spam
Nearly one billion emails were exposed in 2023, affecting one in five email users globally. As 74% of cybersecurity breaches are due to human errors and careless web browsing, it’s important to lay extra safety nets in sidestepping spam threats.
Here are five actionable steps to enhance your spam protection efforts.
1. Use Spam Filters
Phishing attacks are prevalent but only work if they get in your inbox. Google’s spam filter has sophisticated tools to analyse sender reputation, email content, and recipient behaviour. These filters constantly evolve in conjunction with machine learning models to ensure high accuracy in routing emails to your inbox or spam folder.
2. Email Authentication
While DMARC is not the easiest protocol to administer, it instructs mail servers to handle emails that fail SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). This multi-layered approach ensures emails originate from authorised sources and are untampered during transit, protecting you against threats.
3. Blacklist Spam IPs
Use analytics tools that automatically block emails from known malicious IP addresses or domains. Using spam filters and firewalls alongside this helps you avoid spam proactively. As blocked IPs may never reach inboxes, check if your IP isn’t on any blacklist using services like Mailgun to monitor your IP reputation.
4. Avoid Trigger Words in Marketing Emails
Certain words or phrases can trigger spam filters, curtailing deliverability rates for your marketing emails. Using these excessively or inappropriately raises red flags for email service providers:
- Free Gift
- Guaranteed
- Risk-free
- Limited time offer
- Act now
- Click here/below
- Congratulations
- Discount
- Double your money
- Claim Your Prize
5. Train Employees on Phishing
Humans are at the heart of an organisation’s system, so it’s no wonder human error exists in daily operations. As phishing often exploits human error, providing awareness training fosters a culture of security awareness, mostly those that leverage emails.
While there’s a long worklist in the pipeline to protect your digital communication, regular training or phishing simulations help gauge your preparedness for potential threats.
Australian Email Spam Laws and Compliance
While email marketing remains a potent tool, businesses must navigate its associated laws to avoid hefty fines and reputational damage. The CAN-SPAM Act set the rules to protect all consumers from commercial email messages, including advertisements and promotions.
Violators may face fines of up to $51,744 per email that breaches the Act, with the sender and third-party service providers held liable. Recipients can file private lawsuits against violators. Similar to this law is Australia’s Spam Act 2003, which prohibits unsolicited commercial electronic messages.
The latest case under this Act involved the Commonwealth Bank of Australia, which sent unsolicited marketing emails and SMS without a functional unsubscribe facility. This violation resulted in a $7.5 million fine in mid-2024, although smaller cases enforce smaller penalties. So, how can you ensure compliance to avoid this painstaking repercussion?
Businesses must obtain consent before sending marketing emails with accurate header information, subject lines, proper disclosure, and valid physical postal address. Every email must also have easy-to-use opt-out requests.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What percentage of global email is spam?
Nearly 46% of global email traffic is spam in 2023. That’s roughly half of your email inbox potentially filled with unwanted junk containing either harmless or malicious content.
How does spam affect email marketing campaigns?
Spam floods and clutters inboxes, diverting user attention from important messages. When legitimate emails enter user inboxes, they often compete with piles of unsolicited messages, leading to lower open and click-through rates.
What laws regulate spam in Australia?
Spam Act 2003 prohibits sending unsolicited commercial electronic messages, outlining the need for consent before email marketing lands in your inbox. Violations of this act can result in hefty fines due to inaccurate sender contact details and lack of opt-out options.
How can I tell if my emails are being marked as spam?
A sudden drop in email open rates and engagement metrics may indicate that email filters flag your email as spam. Monitoring your domain’s reputation and feedback loops from recipients provides further insights into how users perceive your emails (e.g., malicious, suspicious).
How do spam filters detect spam emails?
Spam filters use sophisticated techniques to detect unwanted emails, including analysing spam keywords, sender reputation, and the recipient’s engagement history. These filters constantly evolve with machine learning models to refine spam detection, ensuring user inboxes remain safe and secure.
Looking for more statistics? Make sure to check out our other statistic articles below!
Written by






