
- Red Search
- Resources
- 6G Statistics
6G Statistics: Market Size, Research, Forecast & Growth
-
 Daniel Law
Daniel Law
Australia’s telecommunications landscape is rapidly accelerating every year. With 5G covering 80% of the country’s population, 6G is already underway as tech giants, telecom providers, and businesses participate in the spectrum’s research and development.
Understanding 6G: The Next Evolution in Wireless Technology
As Australia progresses closer to the next wireless evolution, 6G and its potential applications have begun capturing global attention. Despite 5G being in its deployment phase, the groundwork and development of 6G technology is already ongoing.
As the next emerging technology that will revolutionise most industries and businesses, it’s crucial to understand 6G and how it promises to shape innovation and connectivity.
What is 6G?
Also known as the sixth generation of wireless communication, 6G transmits signals at a much higher frequency than previous generations. As an improvement of the previous generation (5G), 6G promises a much faster data transfer rate with higher capacity, allowing very low latency applications to handle the massive data demands of businesses and future technologies.
How 6G Differs from 5G
5G covers frequencies from 0.4GHz to 114GHz, clocking in at 10 gigabytes per second (Gbps). On the other hand, 6G operates in the Terahertz Band at frequencies between approximately 100GHz to 10THz.
That puts 6G at a higher spot in the electromagnetic spectrum between radio waves and infrared light, a region where transmitters could not generate such radiation until recently.
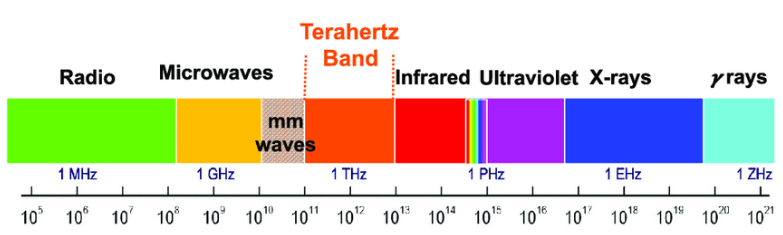
Source: ResearchGate
Tapping the terahertz band, 6G can transfer data at unparalleled speeds compared to its predecessor. In July 2020, 6G mobile broadbands recorded a peak data rate reaching 1000 gigabits per second, roughly 50 times faster than 5G at 20 gigabits per second.
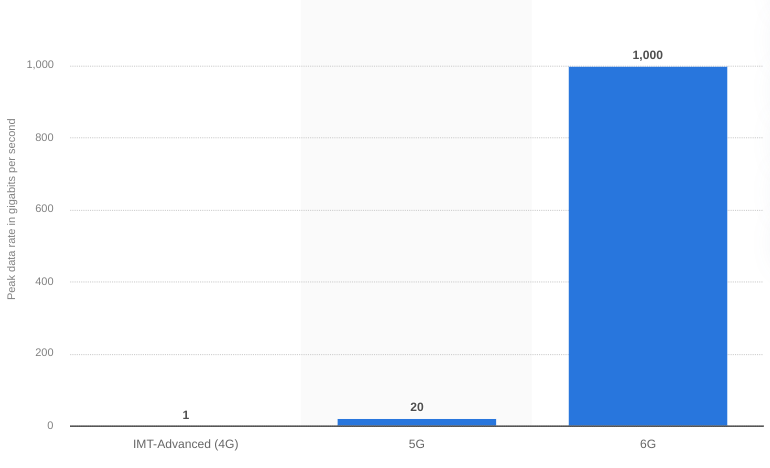 Source: Statista
Source: Statista
Market Size and Global Forecast for 6G Technology
The highly anticipated development and deployment of 6G technology draw significant traction and interest from investors and industries globally.
The global forecast highlights the massive potential of 6G in reshaping industries with new capabilities. It is crucial to understand how the ongoing research, development, and investments drive this technology forward.
Let’s examine current trends to grasp better how close we are to making 6G a reality.
Current Research and Development Investment
Australia is investing AU$10 million to fund the establishment of a 6G R&D Programme, which will fall under the Digital Economy Strategy 2030. This national initiative focuses on how governments, businesses, and the community can cope and seize the benefits of digital transformation.
The government explores the security, viability, and regulatory implications of implementing Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) solutions to promote local telecom market diversification.
The Open Radio Access Network’s main objectives are to:
- Eliminate the siloed nature of the existing RAN market
- Allow smaller competitors to participate and launch their service or customised network
- Deploy, operate, and optimise 6G using automation, AI, and machine learning (ML).
Aside from a proposed R&D program, Australia also invests roughly $20 million to develop a Secure-G Connectivity Test Lab that allows businesses and researchers to test measures, wireless protocols, standards, and software that underpin secure 5G and 6G connections.
These investments and research focus are pivotal in predicting that 6 G will only take about eight years to develop before rolling out to the public—roughly the same time as 5G.
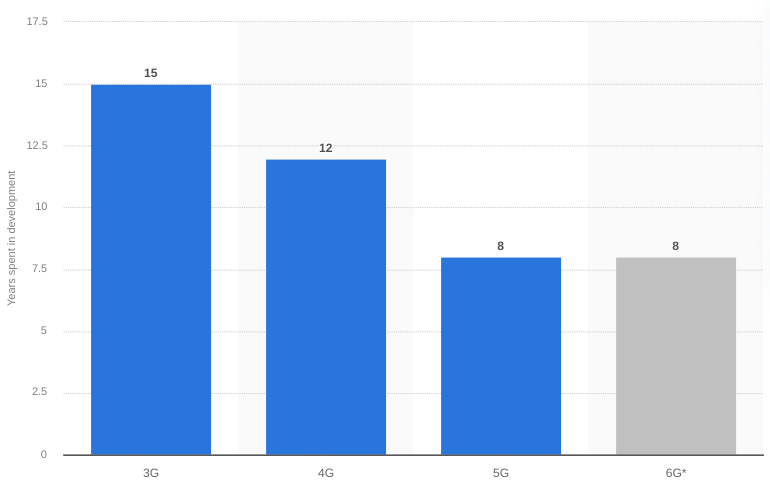
Source: Statista
Projected Market Size of 6G by 2030
Australia needs to catch up with the rest of the developed world regarding fixed broadband speed. As of October 2024, its mobile internet speed is around 103 Mbps for download and 9.61 Mbps for download.
On the other hand, its fixed broadband speed is about 76 Mbps for download and 18.63 Mbps for upload.
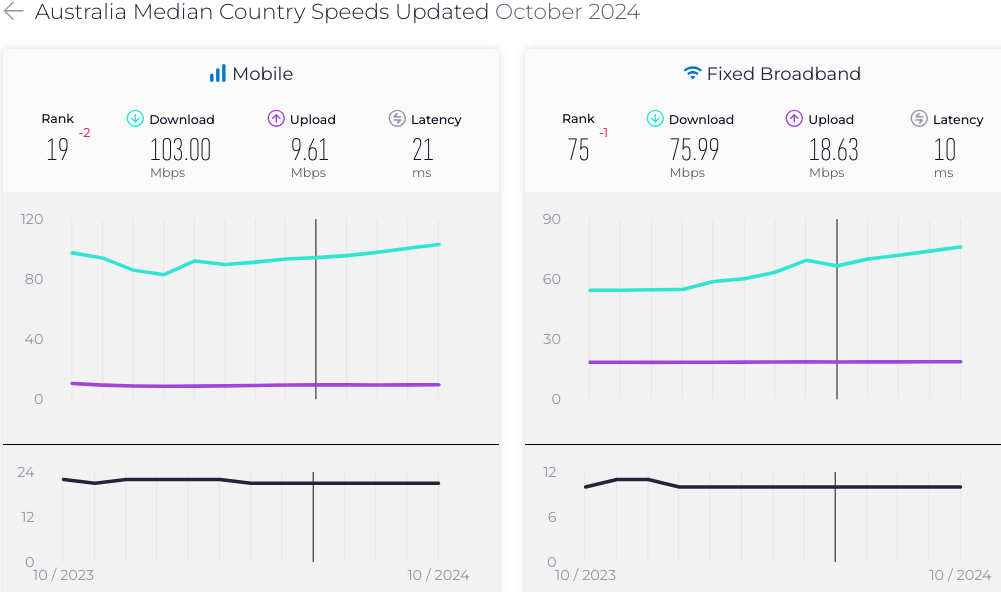
Source: Ookla
Nonetheless, 5G and 6G subscribers in the country are poised to represent roughly 90% of all mobile subscribers by 2030, highlighting the potential of wireless and mobile internet in shaping Australia’s telecom landscape.
The global 6G market was valued at US$5.8 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to grow 34.8% from 2024 to 2030. By 2033, it will reach US$98.2 billion in size.
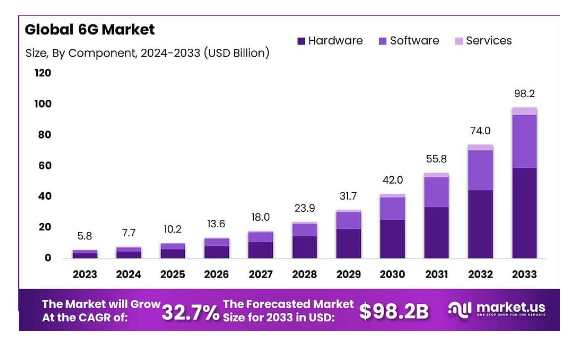
Source: Market.us Scoop
Breaking down by region, North America will be leading the 6G market by 2028 with an estimated US$364.12 million, followed by:
- China: $251.14 million market size
- Europe: $216.21 million
- Asia Pacific & Japan: $91.66 million
- United Kingdom: $57.01 million
- Middle East & Africa: $39.83 million
- South America: $26.69 million
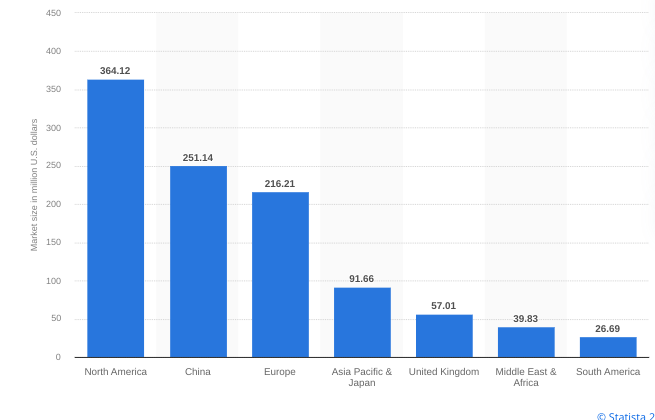
Source: Statista
Leading Players in the 6G Space
The competition to lead and define the 6G space is intensifying, especially as key players and researchers push the boundaries of innovation. Leading tech firms, research institutions, governments, and telecom giants invest heavily in 6G to secure a competitive edge as soon as it rolls out to the public.
1. Nokia
Nokia is at the top of the list, establishing the fundamental technologies for 5G and beyond. Nokia currently heads Hexa-X, a 6G flagship initiative by the European Commission to research and lay the pavement for the next generation of wireless networks.
Nokia Bell Labs expects 6G to be commercially available by 2030. The first phase of standardisation will start in 2025, and 3GPP Release 21—the first release to include 6G technical specifications—will be available by 2028.
2. Ericsson
Like Nokia, Ericsson participates in the Hexa-X project, IMT-2030, and the Next G Alliance. These research collaborations explore potential technologies to establish a cyber-physical world, including 6G networks.
3. Huawei
Huawei recently published its whitepaper, 6G: The Next Horizon, which thoroughly discusses its view of 6G, how it explores 6G key capabilities, new use cases, building blocks, and paradigm shifts in network architecture and air interface.
4. Samsung
Samsung recently announced its new research group, established in the UK, focusing on developing 6G network technologies and 6G-compatible devices. The research group is in addition to the tech firm’s existing global 6G development projects.
Its latest whitepaper on 6G, ‘6G Spectrum: Expanding the Frontier,’ discusses various ways to achieve the company’s 6G vision. Samsung has seven officials in the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), a global organisation uniting telecommunication companies and institutions, including Samsung, Qualcomm, Ericsson, Apple, Nokia, and Huawei.
5. LG
LG successfully set a record for transmitting and receiving 6G THz data wirelessly for over 500 metres outdoors, displaying the capability and expertise in early 6G core technology development with academic institutes. The test occurred at LG Science Park in Magok, Seoul, and was performed jointly with LG U+, South Korea’s second-largest wireless carrier.
6. NTT DOCOMO
DOCOMO has been at the forefront of 5G R&D, actively participating in developing 5G Evolution. With 6G, DOCOMO presented its latest DOCOMO 6G White Paper last January 2020, laying down several technical, societal, and worldview considerations for 6G.
7. Qualcomm
Qualcomm is taking an active role in realising 6G’s potential. It aims to help make 6G a reality with the synergistic potential of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, integrated sensing, and novel green technologies with more capabilities at a significantly lower carbon footprint.
8. AT&T
AT&T once stood at the centre of 5G technology R&D and standards development. It’s currently a founding member of the Next G Alliance, which aims to advance North American wireless technology.
The company also supports launching the 6G Research Centre at the University of Texas.
9. Orange
Orange is actively involved in multiple 6G collaborative projects and initiatives, including the EU flagship Hexa-X project led by Nokia, the NGMN Alliance, and the IOWN Global Forum, which mainly focus on establishing societal and technological standards for new-generation wireless technologies.
Leading telecommunications operator and digital service provider Orange is actively contributing to the design of 6G.
Orange is involved in several 6G collaborative research projects and leading initiatives, including the European flagship Hexa-X project, the NGMN Alliance, and the IOWN Global Forum.
10. Apple
As one of the members of the Next G Alliance (along with AT&T), Apple plays an indirect role in researching and developing 6G. Besides, Apple has been scaling up its team of 6G experts, hinting at creating an in-house 6G modem that is poised to allow Apple to be more self-reliant on 6G and give them more control over the hardware.
Key Growth Drivers for 6G Technology
Developing and investing in 6G boils down to key growth drivers pushing the demand for the technology and its potential advantages, particularly its ultra-fast connectivity, advancements in IoT and AI applications, and a more sustainable infrastructure.
Here are a few key drivers influencing the pace and scale of global 6G research & development:
Demand for Ultra-Low Latency and High-Speed Networks
Each generation of wireless communication has a particular role driven by the demand of the respective period. 1G was known for its voice service, 2G was characterised by voice and text messaging, 3G revolutionised media and internet up to 20 Mbps, 4G took off with its high-speed internet and HD media streaming, as well as video calls, and 5G became the staple for IoT, cloud computing, VR, AR, and other low-latency applications.
Similarly, 6G will bring about a new generation of applications with much lower latency and faster rates, including next-generation extended reality (XR) and big data automation.

Source: LTE Protocol
Expanding Digital Economies:
As global initiatives and long-term goals focus on achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), we expect key players to design 6G networks that are cost—and energy-efficient during deployment, operations, and management.
Keeping 6G core objectives tied to the SDGs allows researchers and institutions to support 6G from design to deployment without hindering the sustainability and social commitments made by the same institutions and governments worldwide.
Technological Advancements Enabling 6G
The key enabling technologies for 6G include:
- A 3D reconfigurable network architecture, combining software flexibility and high-performing hardware for neural network and machine learning
- Extreme Multiple Input Multiple Output (E-MIMO) to support large numbers of high-demand users simultaneously
- Advanced coding & modulation for more streamlined and scalable tests
- Integrated communication & sensing to improve IoT research
- Flexible spectrum sharing to maximise network capacity and resource allocation
- Native intelligence to support AI-native platforms
Emerging Applications of 6G Technology
Holographic Communication
With smart wearables and accessories integrated into wireless networks, the advent of 6G will bring about new interactions, more powerful computing, and connectivity. These contribute to better edge intelligence and computing capabilities, all thanks to 6G’s capacity to support THz communication.
As a result, a more robust wireless network with edge intelligence improves wearables and holographic communication, resulting in a more reliable extended and augmented reality experience.
Advanced IoT Ecosystems
All industries heavily relying on big data management and high-speed data transfer will benefit from 6G’s high bandwidth and fast speed as it operates in the terahertz gap, roughly between 100 GHz and 10 THz.
6G is poised to advance existing IoT applications requiring low-latency and real-time monitoring, such as telesurgery, patient monitoring, and real-time imaging analysis for MRI and CT scans.
Aside from its advantage in medical applications, 6G will also increase the availability of autonomous vehicles as collecting information across thousands of sensors and radars becomes easier, more streamlined, and rapidly processed to maintain a high level of safety.
Space-Based Internet Connectivity
Compared to 5G, 6G improves spectral efficiency and capability for Very Low Earth Orbit (VLEO) satellite networks. As 6G enables very low latency and high-speed data transfer to VLEO satellites, we expect key players to establish a mega satellite constellation that integrates non-terrestrial and terrestrial communications, whether for broadband or IoT services.
Challenges in 6G Adoption
Infrastructure Overhaul Requirements
Like all subsequent generations, unlocking 6G’s massive potential will require extensive deployment of advanced infrastructure that can withstand high data rates at very low latency. It’s worth noting that despite significant efforts, previous wireless communications have not reached about 2.9 billion people globally.
The plethora of use cases and potential of 6G (as discussed in the previous chapter)requires extensive infrastructure deployment that can support high data rates and low latency communications.
Moreover, the internet penetration rate in developed countries as of March 2024 is 87%. Developing countries have a 47% internet penetration rate, while 19% for least developed nations.
That means the advent of 6G may worsen the urban-rural divide, as most infrastructure will focus on highly urbanised areas with high demand for 6G.
Regulatory and Security Concerns
Australia still needs a strategy or national policy for utilising 5G and 6G. This may become a hurdle to realising the full potential of these critical enabling technologies.
6G and newer wireless communications technologies must form part of a broader national strategic framework that encompasses the entire government—allowing Australia to address its strategic gap in terms of mobile technology.
Aside from regulatory concerns, the most critical issues in 6G networks will revolve around data processing, traffic analysis, threat detection, and data encryption. Due to the massive traffic and high-speed data transfer rate, decentralising 6G security systems can mitigate and resolve these security concerns.
That means 6G networks can potentially handle traffic dynamically and locally, implementing security efforts at multiple points to avoid bottlenecks.
Moreover, the Internet of Everything (IoE) and the Internet of Things (IoT), with their wide variety of services and wireless capabilities, make implementing distributed AI, privacy, and security solutions with 6G more challenging.
Security complications and privacy problems may arise as new connected devices switch from 5G to 6G, requiring services from other networks as an interconnected mesh system.
Technological Barriers
With 6G entering the landscape, spectrum availability and management is a growing concern due to the rapid expansion of wireless-based systems and the proliferation of radio communication technologies.
An adequate spectrum for 6G will be pivotal in deploying the 6G network. Spectrum congestion may occur as different parts of the 6G spectrum are used for various technologies and applications, resulting in undercapacity.
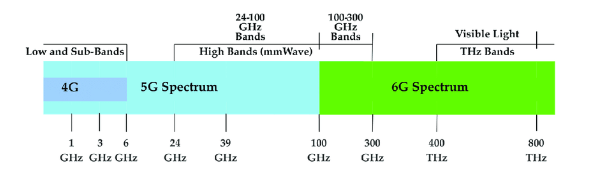
Source: ResearchGate
Many private enterprises advocate for direct spectrum allocation for private networks so they can have better control over their networks and the flexibility to adapt to changing business needs.
However, as 6G is an improvement of 5G, we must consider existing technologies like edge computing, industrial IoT, and hybrid cloud. It’s almost a no-brainer that telecom companies will deploy these in the future, leaving private enterprises to limit their returns on 5G-6G investments.
Preparing for the 6G Revolution: Insights for Businesses
TMT (technology, Media, and telecom) Industry Poised for Transformation
Common online activities, like video and audio streaming, gaming, and video calling, require considerable bandwidth and low latency, challenging exponentially increasing demands.
With 6G, this industry is at the onset of a massive transformation, particularly niches requiring high bitrates like 4K video uploading and large media downloads.
Generative AI
One of the next big things for Australia’s digital world and 6G is the rise of generative AI (Gen AI). Gen AI tools significantly enhance productivity, leading creatives, marketers, and businesses to leverage these tools daily.
Besides, the demand for Gen AI hardware is driving a substantial growth potential in the sector, complementing research and development surrounding 6G wireless technology. Gen AI anticipates investments at around AU$27.5 billion, a sevenfold increase. With specialised hardware and software solutions improving Gen AI efficiency and power consumption, new talent upskilling focuses more on harnessing AI’s full potential.
Why Businesses Should Pay Attention Now
The next wave of wireless technology will integrate sensing and AI capabilities into communication, driving Australia’s future digital economic growth. This will support business applications like ubiquitous intelligence and computing, digital twin technology, and smart industrial applications, paving the way for smarter and more adaptable businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 6G, and when will it be available?
6G is the sixth and latest generation of wireless technology developed to improve 5G. It promises ultra-fast data transfer speed, low latency, and more scalable connectivity for IoT, telecom, VLEO satellites, and other industrial and business applications.
Rollout is expected around 2030. Key players and investors have been conducting ongoing research and development since 2020, and governments are focusing on standardisation and regulation efforts.
How big is the global 6G market?
By 2033, the global 6G market is poised to reach about US$98.2 billion, driven by increasing demands for ultra-reliable networks, low latency, and high capacity transfers across industries and sectors.
What industries will 6G impact the most?
Industries most dependent on 5G networks and cloud services will greatly benefit from 6G. Forecasts predict that 6G will revolutionise healthcare (telemedicine and remote surgeries), transportation (autonomous and remotely controlled vehicles), manufacturing (smart factories, digital plant twins), and smart agriculture (crop digital twin, cloud soil quality, and weather monitoring), alongside ever-expanding IoT applications.
What are the main challenges to 6G adoption?
Existing challenges that impact 6G adoption and rollout include regulatory approval, spectrum allocation within the target frequency range, infrastructure costs to accommodate 6G networks and technological advancements that meet 6G’s performance requirements.
How can businesses prepare for the 6G era?
The wireless technology sector and all industries that rely on it are rapidly changing. Businesses with enough resources should invest in R&D and enhance their digital infrastructure to exploit 6 G’s potential to improve operational efficiency fully.
We also recommend collaborating with industry partners and key players to stay ahead and on top of the rapidly evolving 6G digital wireless ecosystem.
Final Thoughts
With the ever-growing need for digital connectivity, 6G holds immense potential to revolutionise Australian businesses and transform global economies with faster speed, connectivity, and innovation.
Its impact will be significantly more far-reaching than its predecessors, enabling several innovations, including healthcare, transportation, smart cities, and immersive online experiences.
Technology aside, businesses, policymakers, and key innovators must align their strategies and goals to effectively navigate challenges and opportunities that vary between governments and institutions.
6G will be here to stay, and businesses, big or small, can leverage this technology to adapt to changing landscapes and trends. This will allow them to keep up with new challenges and stay ahead of the competition.
Check out more related statistics through our posts below:
Written by
Daniel Law
Daniel Law is the SEO Director at Red Search, a specialist SEO agency based in Sydney, Australia. With over 15 years of experience in the industry, Daniel has a wealth of knowledge and expertise in search engine optimisation (SEO). He is passionate about helping businesses achieve success through effective and sustainable SEO strategies and is dedicated to staying up to date on the latest industry trends and best practices.





